Electronic Health Records (EHRs) have become a foundational element in modern healthcare, promising improvements in patient care, safety, efficiency, and coordination.
*1
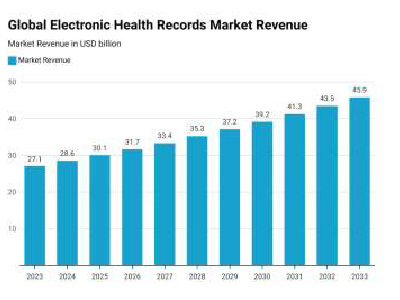
- Estimated at a global market share of $45.9Bn by 2033, almost double the current market size
- Implementation of Electronic Health Records (EHR) has significantly improved various patient outcomes, healthcare is more accessible across age groups and populations
- Inpatient EHR holds 55% of the market share while the remaining 45% is dedicated to outpatient*1
*2

*3
The DataIntelo report highlights that the strength of clinical EHR systems today stems largely from a convergence of regulatory, demographic, and technological forces. The global push toward digitalization in healthcare has increased the demand for centralized, accessible patient information, helping providers improve care quality and safety. Recent studies highlight, on one hand, the rise in chronic diseases, increase doctor visits and a rise in ageing population making the demand for robust software systems that can handle more complex, data intense healthcare ecosystems irrespective of size of the care giving organization.
Although hospital information systems have been integrated for over a decade, persistent myths surrounding EHRs remain a barrier to optimizing system performance and interoperability.
1) EHRs decrease face time with patients
Concern : The focus shifting to entering data and recording information may reduce the actual time spent on patient-provider interaction.
Validation : In primary care, EHRs have been associated with slightly more face time per visit (an extra ~1.3 minutes per visit) and can enhance productivity/efficiency in primary care physician workloads. However, the enhancement due to EHR adoption varies across hysician ages.*4
2) EHRs always lead to a big drop in productivity forever and are expensive for smaller clinics & practises
Concern : It is a common misconception that once EHR is introduced, productivity suffers particularly in regions of high population and daily patient load. Plus the cost factor for a small to mid-size health practise may not be feasible.
Validation : Studies have shown that after EHR implementation, many clinics do experience a drop in productivity (often fewer patient visits) in the short term with declines significantly evident in the first 3-6 months post-implementation.
- Over about 1-2 years, though, many practices see increased revenue, often through more ancillary procedures, despite fewer visits. Better billing capture thanks to improved documentation with increased efficiency over time, and improvements in workflow and support staff use has enabled quicker turnover rate in some cases with long term benefits*5.
- Also, in many cases patient satisfaction remains high or even improves, for instance through better physician attention, clearer explanation of tests and treatments, and enhanced communication with easier access to patient medical history and detailed information*6.
3) Interoperability is "automatic" between EHR systems and digital security with confidential data is a growing concern
Concern : Many believe that once EHRs are in place, systems will seamlessly share patient data across hospitals, clinics, labs, etc., and that privacy risks are minor or already solved.
Validation : Despite regulatory and compliance certifications, systems often lack standardization in data formats, coding systems, and message structures. For example, one lab system may refer to glucose as "GLU," while another uses "Glucose blood," leading to inconsistencies in data interpretation. Additionally, variations across vendors can result in differences in response times, data completeness, and support, further complicating interoperability. These challenges necessitate data mapping and normalization efforts to achieve meaningful data exchange between healthcare systems. However, when HIPAA-certified and properly implemented with one-to-one personalization and digital regulatory checkpoints, data is both secure and easy to use within authorized limits*7.
Customization is the cornerstone of successful EHR integration. While challenges persist, particularly concerning face time with patients, productivity and interoperability during the initial implementation phase, they also offer significant benefits.
Addressing these misconceptions and understanding the realities of EHRs can help healthcare organizations make informed decisions that enhance patient care and operational efficiency. Ultimately, choosing an effective hospital information system requires a clear understanding of its strengths and limitations. By challenging common misconceptions, organizations can adopt solutions that truly support their clinical and administrative missions.

- *1 Pangarkar, T 2025. EHR Industry Statistics 2025 By Digital Record Technology. EHR Industry Statistics and Facts (2025)
- *2 Clinical Ehr Systems Market Report (2025). Clinical Ehr Systems Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033.Clinical Ehr Systems Market Size, Market Share, Companies & Forecast Up To 2033
- *3 Sharma, R (2025). Clinical EHR Market.Clinical EHR Market Report | Global Forecast From 2025 To 2033
- *4Bae, J and Encinosa, W.E. (2016). National estimates of the impact of electronic health records on the workload of primary care physicians. National estimates of the impact of electronic health records on the workload of primary care physicians | BMC Health Services Research | Full Text
- *5 Howley, M. J., Chou, E. Y., Hansen, N., & Dalrymple, P. W. (2015). The long-term financial impact of electronic health record implementation. Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association, 22(2), 443-452. The long-term financial impact of electronic health record implementation - PubMed
- *6 Meyerhoefer, Chad D., Susan A. Sherer, Mary E. Deily, Shin-Yi Chou, Xiaohui Guo, Jie Chen, Michael Sheinberg, and Donald Levick. "Provider and Patient Satisfaction with the Integration of Ambulatory and Hospital EHR Systems." Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association, vol. 25, no. 8, 16 May 2018, pp. 1054-1063.Provider and patient satisfaction with the integration of ambulatory and hospital EHR systems - PMC
- *7 Helixbeat (2025). "FHIR API Integration for Healthcare Systems: Challenges, Solutions, and Case Studies."FHIR API Integration In Healthcare: Challenges & Solutions
